This presentation explores the prevalence, causes, impact, and control of nosocomial (hospital-acquired) infections. It provides both a clinical perspective and real case data from Spanish hospitals. Key points include:
- Definition and scope: Nosocomial infections develop 72+ hours after hospital admission. They affect 5–10% of hospitalized patients and are linked to significant morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs.
- Main types of infections: Urinary Tract Infections (often catheter-related). Bloodstream infections (CR-BSI)
- Impact of COVID-19: An increase in several nosocomial infections during the pandemic was observed, especially in ICU settings.
- Economic burden: Nosocomial infections cost the Spanish healthcare system around €1 billion annually, with individual cases costing from several thousand up to over €40,000 depending on severity.
- Microbial threats: The rise of antibiotic-resistant organisms, including Candida auris, is a growing concern.
- Antimicrobial stewardship: Around 30–50% of antibiotic use is potentially inappropriate. Effective antimicrobial policies and education are essential.
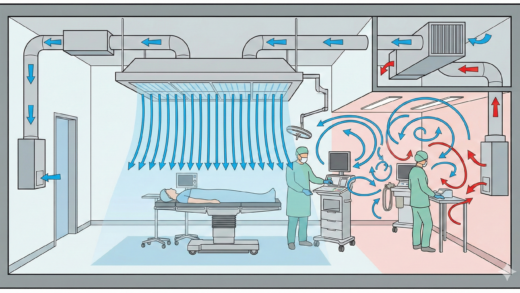
- Infection control strategies: Hand hygiene. Environmental controls. Infection prevention teams and protocols. Engineering solutions (hospital design, air/water safety). Technological innovation and monitoring systems
- Call to action: Emphasizes a multidisciplinary approach, safety culture, and systems-level changes to reduce preventable harm.